简易RPC框架 - 服务订阅、发现模块
1、结构设计
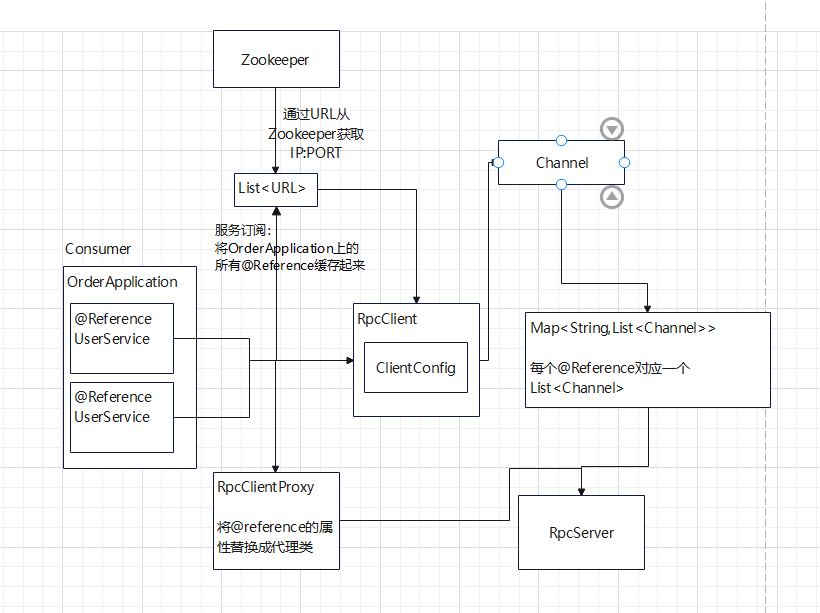
首先先看Rpc客户端的设计思路:
2、实现
这里也是直接上代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
| @Slf4j
public class RpcClientAutoConfiguration implements BeanPostProcessor, ApplicationListener<ApplicationReadyEvent> {
private static NettyRpcClient client;
private volatile boolean needInitClient = false;
private volatile boolean hasInitClientConfig = false;
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
final Class<?> targetClass = bean.getClass();
final Field[] declaredFields = targetClass.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : declaredFields) {
if(field.isAnnotationPresent(RpcReference.class)){
if(!hasInitClientConfig) {
client = new NettyRpcClient();
client.initClientApplication();
hasInitClientConfig = true;
}
needInitClient = true;
final RpcReference annotation = field.getAnnotation(RpcReference.class);
final RpcServiceConfig rpcServiceConfig = RpcServiceConfig.builder()
.group(annotation.group())
.version(annotation.version())
.build();
field.setAccessible(true);
RpcClientProxy rpcClientProxy = new RpcClientProxy(client, rpcServiceConfig);
final Object proxy = rpcClientProxy.getProxy(field.getType());
try {
field.set(bean, proxy);
client.doSubscribeService(field.getType());
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (UnknownHostException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return bean;
}
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationReadyEvent applicationReadyEvent) {
if(needInitClient && client != null){
log.info(" ================== [{}] started success ================== ", client.getClass().getName());
ConnectionHandler.setBootstrap(client.getBootstrap());
client.doConnectServer();
}
}
}
|
值得注意的是,我们这里用到了ApplicationContext的事件机制,因为需要需要实现通道连接时保证所有的@Reference都已进行服务订阅,查了很多资料,学到了这个方法。首先该类实现了ApplicationListener,那么每当ApplicationContext发布ApplicationEvent时,ApplicationListener Bean将自动被触发。我们这里监听的是ApplicationReadyEvent事件,当上下文已经准备完毕的时候触发onApplicationEvent()方法。
通过ApplicationContext的事件机制,我们就可以实现这个效果:Spring扫描整个类的@Reference属性,然后进行服务订阅,将@Reference对应的信息封装成URL对象。当上下文准备完毕,意味着所有的@Reference属性都已进行订阅,此时会触发onApplicationEvent()方法,将Client与每个@Reference属性对应的RpcServer建立一个Channel,之后当需要远程调用时,就可以在代理类中获取对应的Channel进行通信。
在这里,将URL和代理类贴出来,方便大家理解:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| @AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@Data
public class URL {
private String applicationName;
private String serviceName;
private Map<String, String> parameters = new HashMap<>();
public void addParameter(String key, String value) {
this.parameters.putIfAbsent(key, value);
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
| @Slf4j
public class RpcClientProxy implements InvocationHandler {
private static final String INTERFACE_NAME = "interfaceName";
private final RpcRequestTransport rpcRequestTransport;
private final RpcServiceConfig rpcServiceConfig;
public RpcClientProxy(RpcRequestTransport rpcRequestTransport, RpcServiceConfig rpcServiceConfig) {
this.rpcRequestTransport = rpcRequestTransport;
this.rpcServiceConfig = rpcServiceConfig;
}
public <T> T getProxy(Class<T> clazz){
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(clazz.getClassLoader(), new Class<?>[]{clazz}, this);
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
if(method.getName().equals("toString")){
return null;
}
log.info("开始执行方法: [{}]", method.getName());
RpcRequest rpcRequest = RpcRequest.builder()
.requestId(UUID.randomUUID().toString())
.parameters(args)
.methodName(method.getName())
.interfaceName(method.getDeclaringClass().getName())
.paramTypes(method.getParameterTypes())
.group(rpcServiceConfig.getGroup())
.version(rpcServiceConfig.getVersion())
.build();
RpcResponse<Object> rpcResponse = null;
if (rpcRequestTransport instanceof NettyRpcClient) {
CompletableFuture<RpcResponse<Object>> completableFuture = (CompletableFuture<RpcResponse<Object>>) rpcRequestTransport.sendRpcRequest(rpcRequest);
rpcResponse = completableFuture.get();
}
if(rpcRequestTransport instanceof SocketRpcClient) {
rpcResponse = (RpcResponse<Object>) rpcRequestTransport.sendRpcRequest(rpcRequest);
}
check(rpcRequest, rpcResponse);
return rpcResponse.getData();
}
private void check(RpcRequest rpcRequest, RpcResponse rpcResponse){
if(rpcResponse == null){
throw new RpcException(RpcErrorMessageEnum.SERVICE_INVOCATION_FAILURE, INTERFACE_NAME + ":" + rpcRequest.getInterfaceName());
}
if(!rpcResponse.getRequestId().equals(rpcRequest.getRequestId())){
throw new RpcException(RpcErrorMessageEnum.REQUEST_NOT_MATCH_RESPONSE, INTERFACE_NAME + ":" + rpcRequest.getInterfaceName());
}
if(rpcResponse.getCode() == null || !rpcResponse.getCode().equals(RpcResponseCode.SUCCESS.getCode())){
throw new RpcException(RpcErrorMessageEnum.SERVICE_INVOCATION_FAILURE, INTERFACE_NAME + ":" + rpcRequest.getInterfaceName());
}
}
}
|
至于服务订阅、通道连接的代码大家可以根据自己的需要进行设计,我这里就不再描述了。
至于负载均衡,可以在通道连接的时候设计,也可以按大家的想法来。



